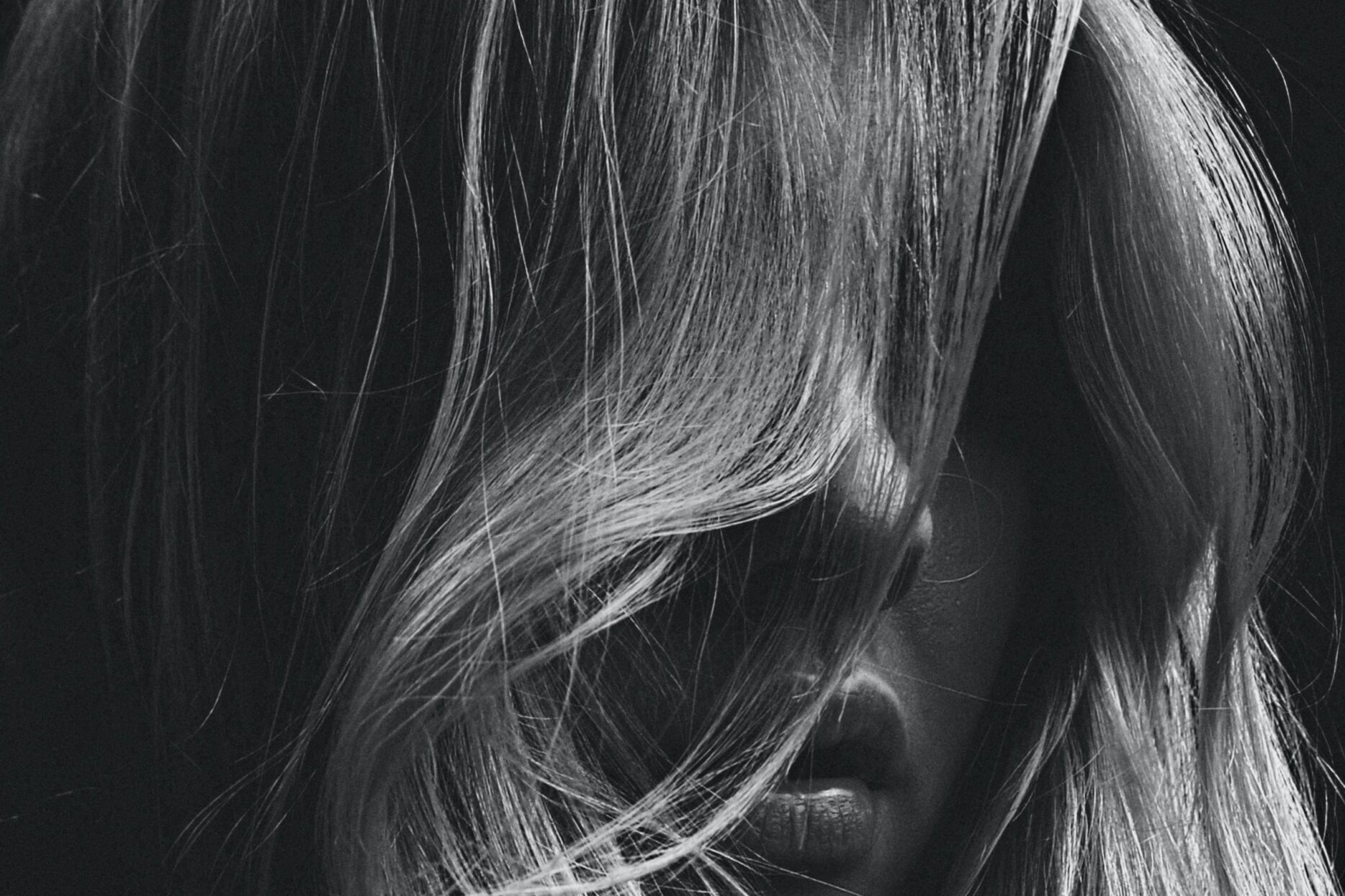
Along with the well-known menopausal symptoms, including mood swings, sleeplessness, and hot flashes many women may also struggle with hair loss and look for how to reverse thinning hair after menopause, a problem that is sometimes overlooked. This specific symptom can significantly affect self-esteem, causing extreme distress.
The prevalence of menopausal hair loss is surprisingly high, affecting a larger percentage of women than one might imagine. Statistics indicate that around 40 percent of women experience hair loss during menopause. It’s important to remember that this condition is typically not permanent, and there are numerous natural techniques to stimulate hair regrowth and preserve its health.
We’ll explore the underlying causes of menopausal hair loss and the best approaches to managing and how to reverse thinning hair after menopause.
Causes of Hair Thinning During Menopause:
- Hormonal Changes: The decline in estrogen levels that accompanies menopause can impact the hair growth cycle. Reduced estrogen can cause hair thinning as it stimulates hair growth.
- Aging: Variations in hair density and texture can result from aging itself. Hair may grow finer, thinner, and become more prone to damage as you age.
- Genetics: Your family history plays a significant role in your likelihood of experiencing hair thinning or pattern baldness.
- Stress: Chronic stress can exacerbate hair loss, so managing stress is crucial.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: A poor diet can also impact the condition of your hair. Ensure that you are receiving adequate amounts of iron, vitamin D, and biotin.
Managing Hair Thinning During Menopause:
- Scalp Care: Proper scalp care is essential. Gently massage your scalp to stimulate blood flow and promote hair growth. Avoid harsh hair treatments and products that can damage your hair.
- Topical Treatments: Over-the-counter minoxidil (Rogaine) is an FDA-approved topical treatment that may help promote hair regrowth.
- Wigs and Hairpieces: If your hair loss is substantial and you’re not satisfied with the results of other treatments, consider wigs or hairpieces to enhance your appearance and confidence.
- Support Groups: Joining support groups or seeking counseling can help you cope with the emotional impact of hair thinning during menopause.
- Prescription Medications: In some cases, prescription medications like spironolactone may be recommended to manage hair thinning.
How to Reverse Thinning Hair after Menopause:
- Gentle Handling: Be gentle when washing, brushing, and styling your hair to minimize breakage.
- Avoid Heat and Chemicals: Limit the use of heated styling tools and harsh chemicals that can damage your hair.
- Choose the Right Shampoo: Use a mild, sulfate-free shampoo suitable for your hair type.
- Scalp Care: Keep your scalp clean and healthy. Consider using scalp massage or low-level laser therapy.
- Consult a Healthcare Professional: If you’re experiencing significant hair thinning, consult a healthcare provider to rule out any underlying medical conditions or hormonal imbalances.
It’s crucial to keep in mind that hair thinning is a typical and normal part of menopause. While you might not be able to fully reverse it, you can manage and enhance the state of your hair by following the guidance provided above and consulting a healthcare provider as needed.”